Da ja diese Woche der Safer Internet Day war, möchte ich mal beschreiben, welche Maßnahmen ich auf meinen Rechnern getroffen habe, um möglichst sicher im Internet unterwegs zu sein.
SAMETIME 9.0: Latest Published Versions
As there already have been several updates and hotfixes for Sametime 9.0 released it is not easy to find out which the latest versions of the Sametime components are. To make that easier you can check out the summary on this web page.
Security hole in Firefox and Chrome allows leaking of IP address
A security hole in Firefox and Chrome allows websites to determine a web user’s real IP address, even when using a VPN:
“Firefox and Chrome have implemented WebRTC that allow requests to STUN servers be made that will return the local and public IP addresses for the user. These request results are available to javascript, so you can now obtain a users local and public IP addresses in javascript. This demo is an example implementation of that.
Additionally, these STUN requests are made outside of the normal XMLHttpRequest procedure, so they are not visible in the developer console or able to be blocked by plugins such as AdBlockPlus or Ghostery. This makes these types of requests available for online tracking if an advertiser sets up a STUN server with a wildcard domain.”
See more details here on this page.
https://torguard.net/blog/browser-security-vulnerability-may-allow-real-ip-leak/
On this site you can check if your broser is affected. With your VPN connected browse to this website and you should see your real IP address in addition to your VPN provider address:
https://diafygi.github.io/webrtc-ips/
How to fix:
For Google Chrome download and install this extension to disable WebRTC.
For Firefox goto “about:config” and set the configuration setting “media.peerconnection.enabled” to “false”.
Scripting Source for IBM Connections
I am not sure if everybody is aware of this great collection of Websphere scripts to simplify some of the IBM Connections configuration tasks. If not, you really should have a look:
Connections Administration & Scripting 101
Thanks to Christoph for his hard work.
Der papierlose Haushalt / das papierlose Büro
Naja, soweit sind wir dann doch noch nicht ganz. Aber ich möchte doch mal berichten, was sich in Sachen “Papierloser Haushalt” getan hat. Im Mai 2014 habe ich mal wieder (es gab schon ein paar Anläufe in der Vergangenheit) versucht, den ganzen Papierkram hier zuhause, der sich über die Jahre so angesammelt und viele Meter Regalplatz mit Ordnern verschwendet, irgendwie wegzubekommen. Wenn ich die letzten Monate so zurückblicke, war dieser Versuch doch recht erfolgreich.
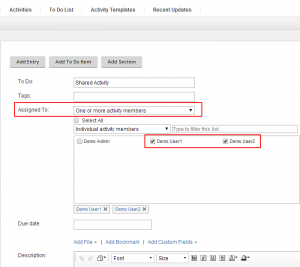
IBM Connections 5.0: Assign Activity tasks to multiple people
Starting with IBM Connections 5.0 you can assign tasks within an activity also to multiple people at once.
A task will be marked as completed once all assigned users have marked the item complete for themselves. An activity owner can also mark the activity complete in general. In this case he will get a warning message:
“Are you sure you want to mark this To Do Item as complete? If you are an assignee and want to complete your own status, you can click the checkbox before your name under this To Do Item.”
To enable this new feature you need to uncomment the following line in “/opt/IBM/WebSphere/AppServer/profiles/Dmgr01/config/cells/connectionsCell/LotusConnections-config/oa-config.xml” and set the value to true:
<property name="feature.multiAssignment.enabled">true</property>
Installing 32-bit Oracle database client for IBM Connections (Cognos)
For the Cognos part of IBM Connections together with an Oracle database you need to install the 32-bit Oracle database client on your Cognos node. Cognos is only supporting the “Runtime-Client” and not the smaller “InstantClient”, so make sure you choose the right one.
Below I describe the steps how to install the client on your Cognos node:
Error starting Cognos server with Oracle as database
After installing the Cognos server for IBM Connections 5.0 together with Oracle JDBC driver, Cognos did not start up although there was no error message in the SystemOut.log. However looking into the Cognos error log (“/opt/IBM/Cognos/CognosBI/logs/cogserver.log”) I saw the following error message:
Umrechnungsgebühren von Paypal sparen
Ich zahle vieles per Paypal weil ich dann nicht überall meine Kreditkarteninformationen hinterlegen muss. Bei Zahlungen in Fremdwährungen rechnet Paypal allerdings standardmäßig selbst den Betregg in EURO um und kassiert dabei ca. 3% Umrechnungs-Gebühren. Mir war irgendwie bislang nicht klar, dass man das auch umstellen kann. Das macht man wie folgt:
- Anmelden bei Paypal
- Aufrufen des eigenen Profils durch Klicken auf das Zahnrad oben rechts:
- Unter “Zahlungen” auf “PayPal-Zahlungen per Händlerabbuchung” klicken:

- Dann auf “Verfügbare Zahlungsquellen festlegen” klicken:
- Nun auf “Umrechnungsoptionen” klicken:
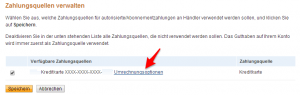
- Hier die Option “Die Rechnung in der Währung ausstellen, die auf der Rechnung des Verkäufers angegeben ist” auswählen und dann mit “Senden” bestätigen:
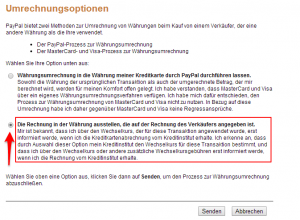
Damit sollte dann in Zukunft die Umrechnung durch die Kreditkartenfirma durchgeführt werden, was günstiger sein sollte (Meine DKB-Kreditkarte berechnet z.B. ein Auslandseinsatzentgelt von 1,75%).
Forwarding mails to Google Account
All my mails are received by my own mail server and are then forwarded to my Google account (as I am using Google Mail as my mail client). Unfortunately if you just forward mails with POSTFIX you might also forward incoming spam mails which Google does not like. It can be that Google thinks you are a spam sender and blacklist your server.
I have found this blog entry which describes a way to correctly set the envelope address of forwarded mails:
So in summary this is what I did:
[codesyntax lang=”bash”]
# download and compile the software
cd ~
wget https://github.com/roehling/postsrsd/archive/master.zip
unzip master
cd postsrsd-master/
make
sudo make install
[/codesyntax]
Then added the following lines to /etc/postfix/main.cf:
[codesyntax lang=”text”]
sender_canonical_maps = tcp:127.0.0.1:10001
sender_canonical_classes = envelope_sender
recipient_canonical_maps = tcp:127.0.0.1:10002
recipient_canonical_classes= envelope_recipient,header_recipient
[/codesyntax]
Then I started the SRS daemon and reloaded the POSTFIX configuration:
[codesyntax lang=”bash”]
# Start SRS daemon
sudo service postsrsd restart
#Reload postfix
sudo service postfix reload
[/codesyntax]
I did not need to add the SRS daemon to startup as it seems to be automatically started already.
As I forward all mail from my server to Expurgate/Spamfence for spam checking I also neeeded to add the Expurgate servers to my SPF domain record so that Google accepts mails sent by my mail server via Expurgate to Google. This is the PSF record I am using for my domain “urspringer.de”:
[codesyntax lang=”text”]
v=spf1 a mx a:mx.expurgate.net ip4:87.230.85.144 ip6:2a01:488:66:1000:57e6:5590:0:1 include:expurgate.net ~all
[/codesyntax]
Currently it seems to look fine as Google verifies the SPF record although the mails are forwarded twice:
[codesyntax lang=”text”]
Return-Path: <SRS0+WJa2=BP=googlemail.com=samoel2406@urspringer.de>
Received: from mx.expurgate.net (mx.expurgate.net. [194.145.224.20])
by mx.google.com with ESMTPS id ft4si45524597pdb.17.2014.12.27.06.00.52
for <michael.urspringer@gmail.com>
(version=TLSv1.2 cipher=RC4-SHA bits=128/128);
Sat, 27 Dec 2014 06:00:53 -0800 (PST)
Received-SPF: pass (google.com: domain of SRS0+WJa2=BP=googlemail.com=samoel2406@urspringer.de designates 194.145.224.20 as permitted sender) client-ip=194.145.224.20;
Authentication-Results: mx.google.com;
spf=pass (google.com: domain of SRS0+WJa2=BP=googlemail.com=samoel2406@urspringer.de designates 194.145.224.20 as permitted sender) smtp.mail=SRS0+WJa2=BP=googlemail.com=samoel2406@urspringer.de;
dkim=pass header.i=@googlemail.com
[/codesyntax]
Update:
If you cannot start the service in Debain 8 and higher () you need to enable the service first with
[codesyntax]
systemctl enable postsrsd
[/codesyntax]